Weight Testing for Lifting Equipment

Weight Testing
Introduction to Weight Testing
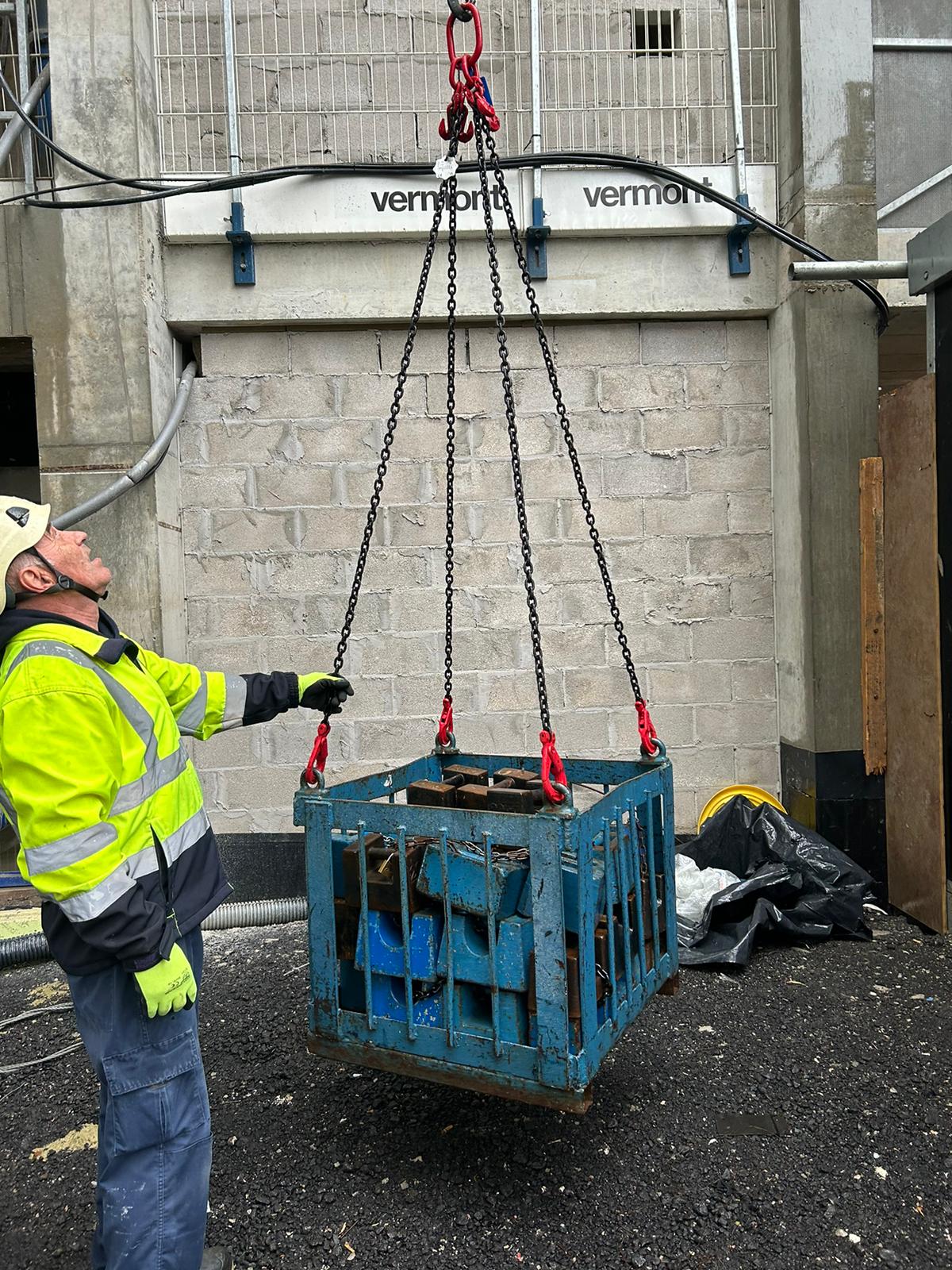
Weight testing, often referred to as a load test or proof load test, is an essential procedure for evaluating the safety and operational performance of lifting equipment. This process involves testing cranes, hoists, lifting rigs, and similar machinery with a specified weight to ensure they can safely handle the loads they are rated for under real-world conditions. Weight tests confirm that the equipment is in optimal working condition, adheres to safety standards, and operates reliably.
This guide explores the purpose, types, procedures, and benefits of weight testing to highlight its critical role in ensuring workplace safety and regulatory compliance.
Purpose of a Weight Test
Weight testing is primarily conducted to verify the operational capabilities, strength, and safety of lifting equipment. It provides a realistic assessment of how the equipment will perform under standard and extreme conditions. Below are the key purposes of a weight test:
Verifying Load Capacity and Strength
- The test ensures that the equipment can handle its rated maximum load safely, as specified by the manufacturer or design guidelines.
- It replicates the conditions the equipment will encounter during normal operations, confirming its ability to perform without failure.

Testing Structural Integrity
- Weight tests evaluate the structural components of lifting equipment, including frames, support mechanisms, hoists, pulleys, and cables, to ensure they can withstand operational forces.
- The procedure identifies any weaknesses, such as cracks, deformation, or stress points, that could compromise the equipment’s reliability.

Ensuring Safety Mechanisms Work Correctly
- Critical safety features, including overload protection devices, emergency stops, limit switches, and braking systems, are assessed under load conditions to confirm they function as intended.
- This step ensures the equipment remains within safe operating limits and that safety systems effectively prevent or mitigate risks during operation.

Checking Load Distribution and Stability
- Proper load distribution is vital to prevent tipping, swaying, or component stress. The test confirms that loads are evenly distributed across slings, hooks, and lifting points.
- It also ensures the equipment maintains stability throughout lifting, holding, and lowering processes, even under challenging conditions.
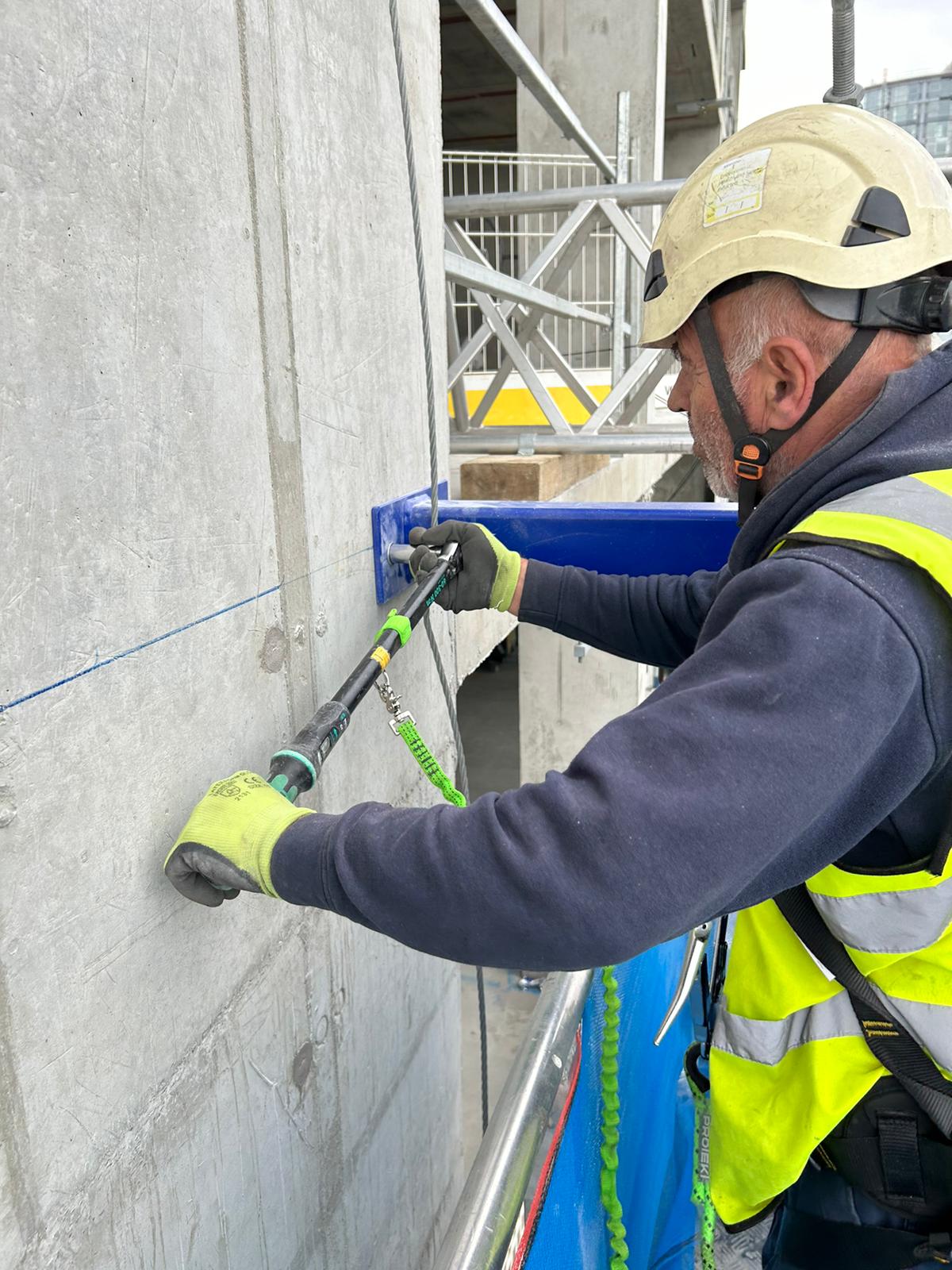

Skyform Limited - Your Trusted Partner in Access Cradle Hire and Load Testing.
Types of Weight Tests
Different types of weight tests are conducted to evaluate various aspects of lifting equipment performance.
- Purpose: Tests the equipment’s resilience by applying a load greater than its rated capacity (typically 125%).
- How It Works: A load exceeding the standard capacity is applied briefly to identify potential failure points or structural weaknesses.
- Example: For equipment rated for 10 tons, a proof load test might involve lifting 12.5 tons to ensure it can handle unexpected overloads.
- Purpose: Evaluates the equipment’s ability to lift, move, and lower loads in a realistic operational context.
- How It Works: Conducted with a load close to the equipment’s rated capacity, this test examines performance features such as responsiveness, stability, and control.
- Purpose: Assesses the equipment’s performance during movement, including hoisting, swinging, and lowering loads.
- How It Works: A load is moved dynamically to simulate operational forces, including swings, jerks, and accelerations, testing the system’s stability and safety mechanisms.
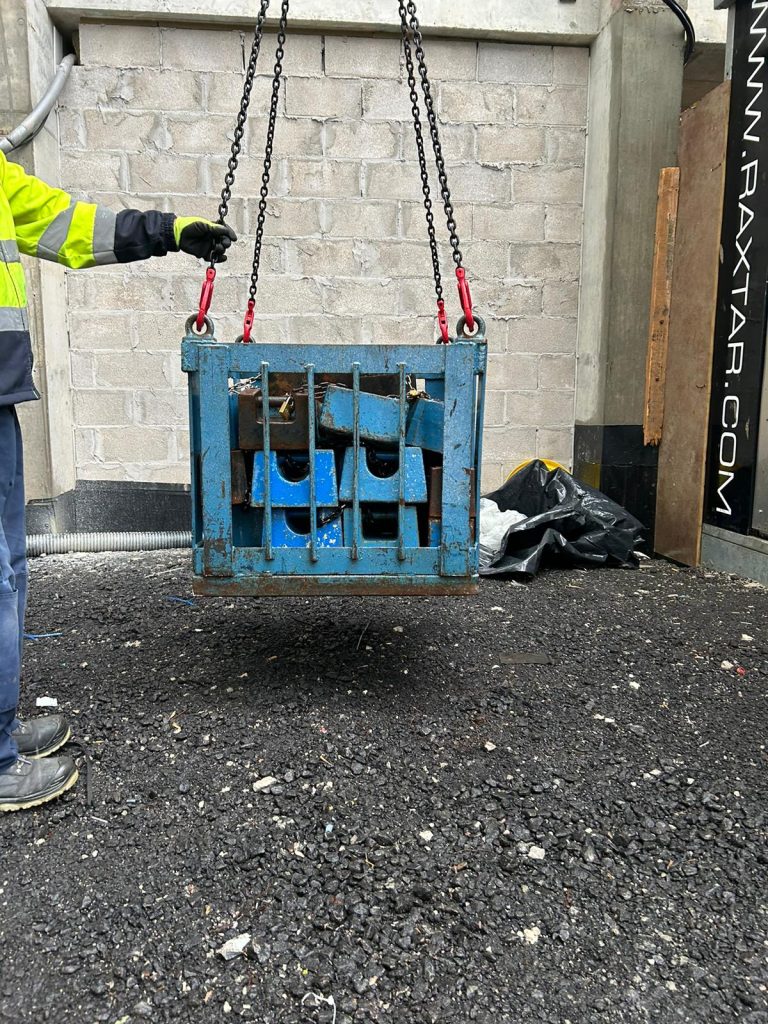
- Purpose: Verifies structural strength and stability by applying a fixed load without movement.
- How It Works: A weight is applied and held in place for a specified duration to confirm that the equipment remains stable and free from deformation or failure.

When Should Weight Testing Be Performed?
Initial Setup
Before putting new equipment into service, conduct a weight test to verify its performance and compliance with design specifications.
Post-Maintenance or Repairs
Test equipment after significant maintenance, repairs, or component replacements, such as hoist motors or cables, to ensure safety and functionality.
Periodic Inspections
Perform regular weight tests (annually or as per usage frequency) to maintain ongoing safety and compliance.
Before Critical Lifts
Conduct weight tests before handling critical or high-risk lifts to confirm the equipment’s readiness and reliability.
Benefits of Weight Testing
Safety
Assurance
Confirms that the equipment can handle its rated loads without risk of failure, protecting workers and assets.
Regulatory
Compliance
Meets industry standards and legal requirements (e.g., OSHA, ASME) for lifting equipment safety.
Early Detection
of Issues
Identifies wear, structural weaknesses, or malfunctions early, preventing costly repairs or on-site accidents.
Improved Equipment
Longevity
Regular weight tests help maintain equipment in peak condition, extending its operational life and reducing downtime.
